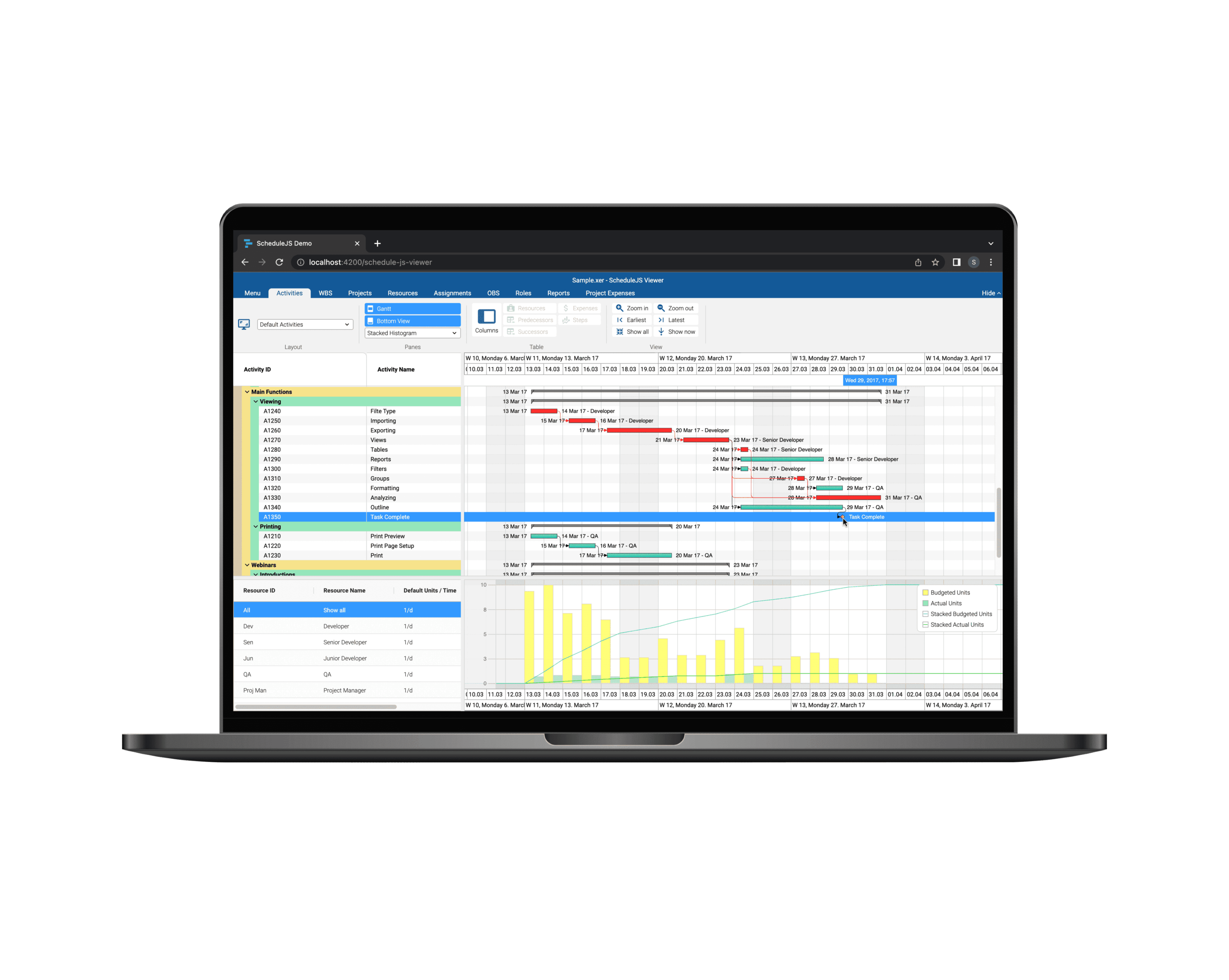
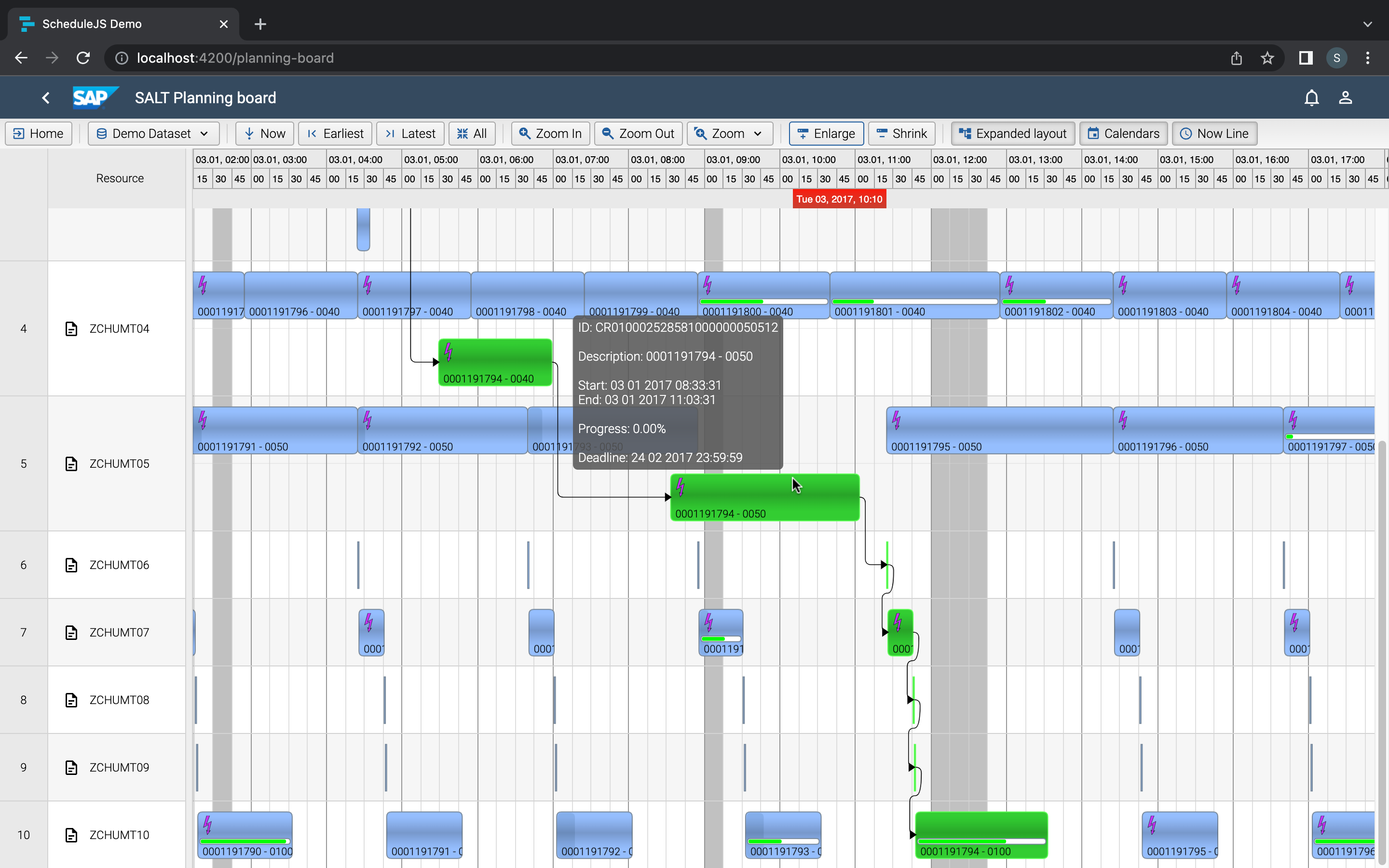
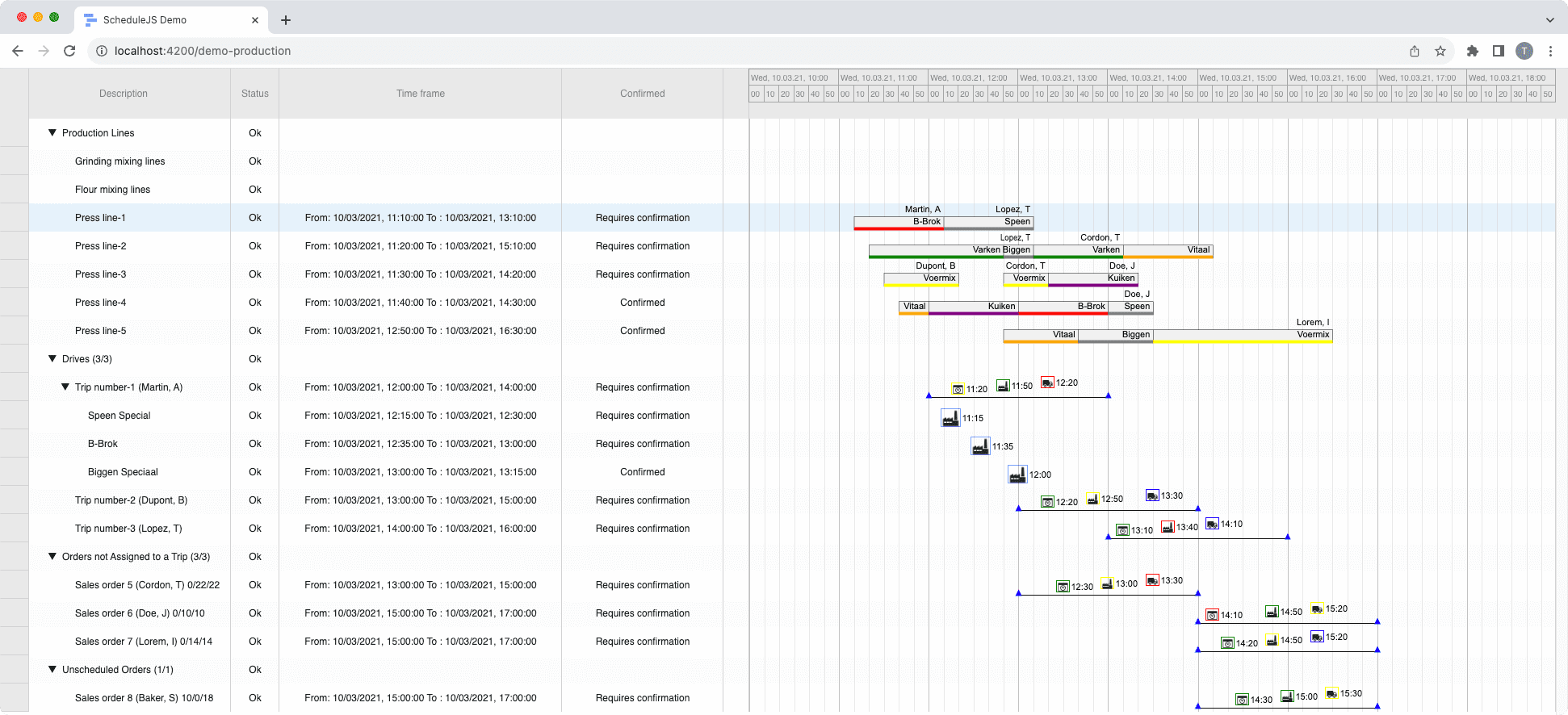
Build custom tree tables in ScheduleJS using schedule-info-column-header-cell and schedule-info-column-row-cell components.

Angular 16 vs Angular 18 : un comparatif des nouveautés
May 15th, 2025 - 5-6 minutes read
Introduction
The Angular framework, developed by Google, is evolving rapidly at a pace of about two releases per year. Each update brings new features, optimizations, and paradigm shifts. Among them, Angular 16 (May 2023) marked a major milestone by introducing signals, a new approach to reactivity that changed the way state is managed in applications. One year later, Angular 18 (May 2024) continued this momentum by consolidating these advances while opening up new possibilities, particularly with the Zoneless mode.
Angular 16: The Revolution of Signals
Before Angular 16, reactivity in Angular was mainly based on RxJS et Observables. While powerful, this model required a certain level of expertise and introduced additional complexity, especially when dealing with simple state management. Angular 16 introduced signals, a more straightforward and intuitive reactive API that makes it possible to track and update values seamlessly.
A signal is a reactive value that can be read like a function and updated through dedicated methods (set, update). For example, a counter can be written in a much more concise way:
With Angular 16, signals were still in developer preview, but they already represented a significant breakthrough. They simplified local state management, improved performance by reducing the number of change detection cycles, and paved the way for finer-grained reactivity in Angular.
Angular 18: Optimization and Control with Zoneless
Angular 18 did more than just consolidate existing features. It introduced a particularly ambitious innovation: the mode Zoneless. Since the very beginning, Angular has relied on Zone.js to intercept events and trigger UI updates. This approach is robust, but it can become costly in terms of performance, especially in large-scale applications.
With Angular 18, it is now possible to run Angular without Zone.js. In mode Zoneless, it’s the developer who explicitly triggers change detection. This provides greater control and reduces the number of unnecessary cycles.
This approach helps avoid the constant triggering of rendering cycles and improves the scalability of applications. For now, the mode Zoneless is still experimental, but it offers a concrete glimpse into the future of Angular.
Zone Coalescing: An Automatic Optimization
Another advancement in Angular 18 is zone coalescing, which is now enabled by default. This optimization groups multiple events into a single change detection cycle. For example, if a user quickly types text into several fields, Angular won’t recalculate the UI after each keystroke but will instead combine the changes.
In this scenario, Angular 18 handles updates more intelligently, making the application smoother without requiring any code changes from the developer.
Async / Await and Asynchronous Handling
Angular 16 already handled asynchronous operations through Observables et le async pipe. Angular 18 goes a step further by allowing developers to use await directly in templates — but only in mode Zoneless.
This evolution makes writing asynchronous code more natural and closer to modern JavaScript, improving readability and reducing the need for complex solutions to handle promises.
Compatibility with TypeScript
Angular 16 was based on TypeScript 5.2, while Angular 18 integrates TypeScript 5.4. This upgrade brings:
-
Stricter typing
-
Improved autocompletion in IDEs
-
Faster compilation performance
These improvements directly benefit developers, providing a more modern et safer environment for their projects.
Angular 16 vs Angular 18: Comparison Table
| Fonctionnalités | Angular 16 | Angular 18 |
|---|---|---|
| Signals | Introduced in preview | Still present, better integrated, stabilization coming soon |
| Zoneless | Not available | Developer preview, more control and performance |
| Zone Coalescing | Optional | Enabled by default |
| Async / Await | Through async pipes only | Direct support in templates (mode Zoneless) |
| TypeScript | v5.2 | v5.4 |
| Performance | Gains thanks to signals | Automatic optimizations + Zoneless |
| Developer Experience | New reactivity | More control, enhanced diagnostics |
Conclusion
The comparison between Angular 16 et Angular 18 highlights two complementary steps in the framework’s evolution. Angular 16 introduced signals, a major innovation that transformed the way reactivity is handled. Angular 18, on the other hand, did not aim to revolutionize the API but rather to optimize its internal workings and prepare for the future with mode Zoneless et zone coalescing enabled by default.
In summary:
-
Angular 16 opened a new era with signals.
-
Angular 18 strengthened performance and gave developers more control over the rendering cycle.
Migrating to Angular 18 therefore allows teams to benefit from automatic optimizations, remain compatible with the latest TypeScript advancements, and most importantly, prepare projects for the major changes that will stabilize in Angular 20.
Plus d'articles sur la mise en œuvre
Unlock flexible row management in ScheduleJS: control individual row heights, mix GanttLayout and ChartLayout in the same view.
Master drag and drop in ScheduleJS: render activities while dragging, access the drag canvas via DragViewTransversalSystemLayers.
ScheduleJS 1.4 release notes. A step forward towards modern Angular app building.
Angular 16 vs Angular 18 comparison: discover what's new in Angular, the arrival of signals, Zoneless mode, zone coalescing, and their impact on your projects.
Discover the Angular Rome Conference: workshops, domain-driven design, signals, state management, micro frontends.
Discover Angular 18: zoneless mode, zone coalescing, native await, and TypeScript 5.4 compatibility.
Le TOP 3 des diagrammes de Gantt JavaScript. Découvrez leurs caractéristiques, avantages et inconvénients pour choisir le meilleur outil pour votre projet.
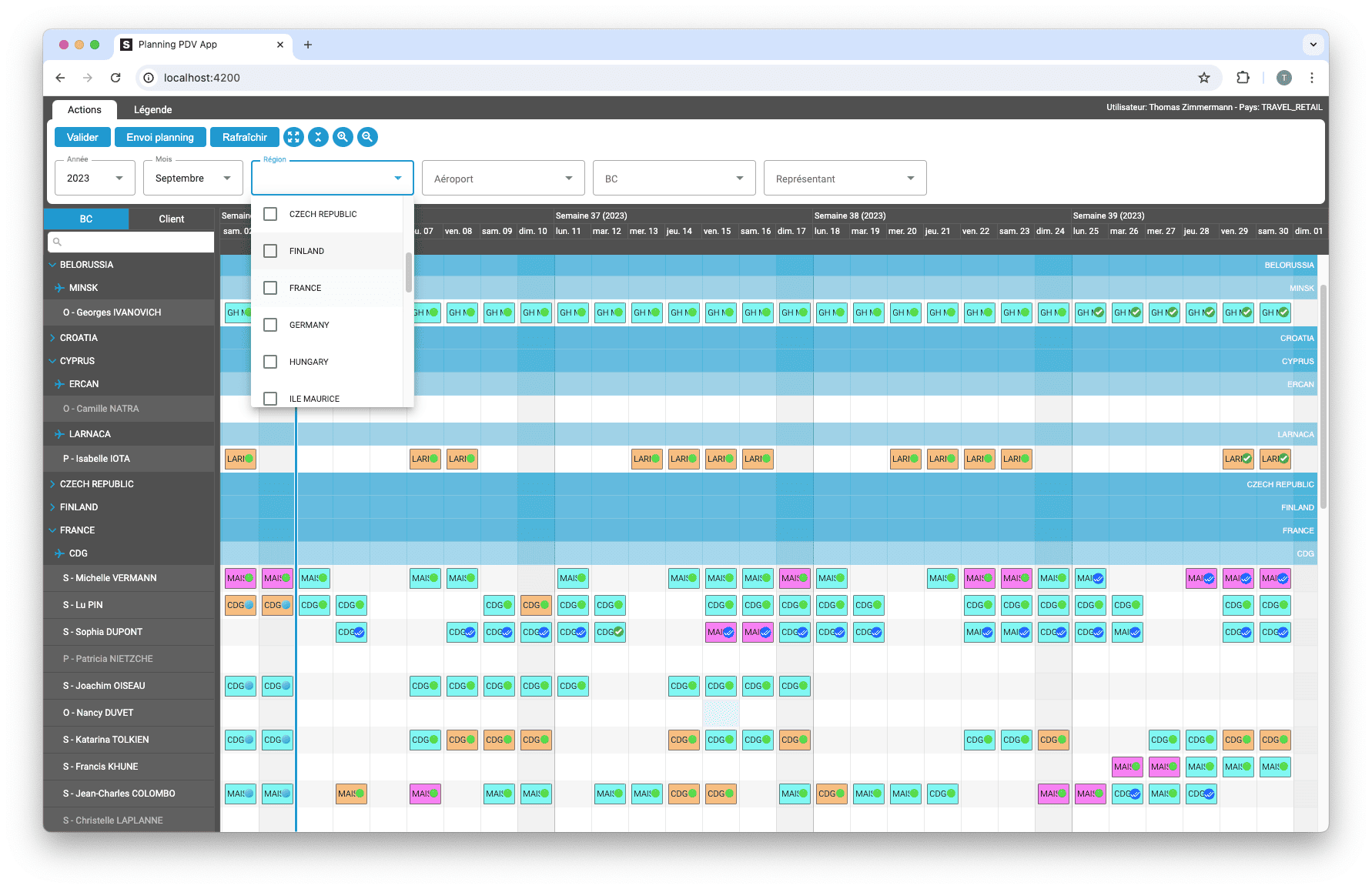
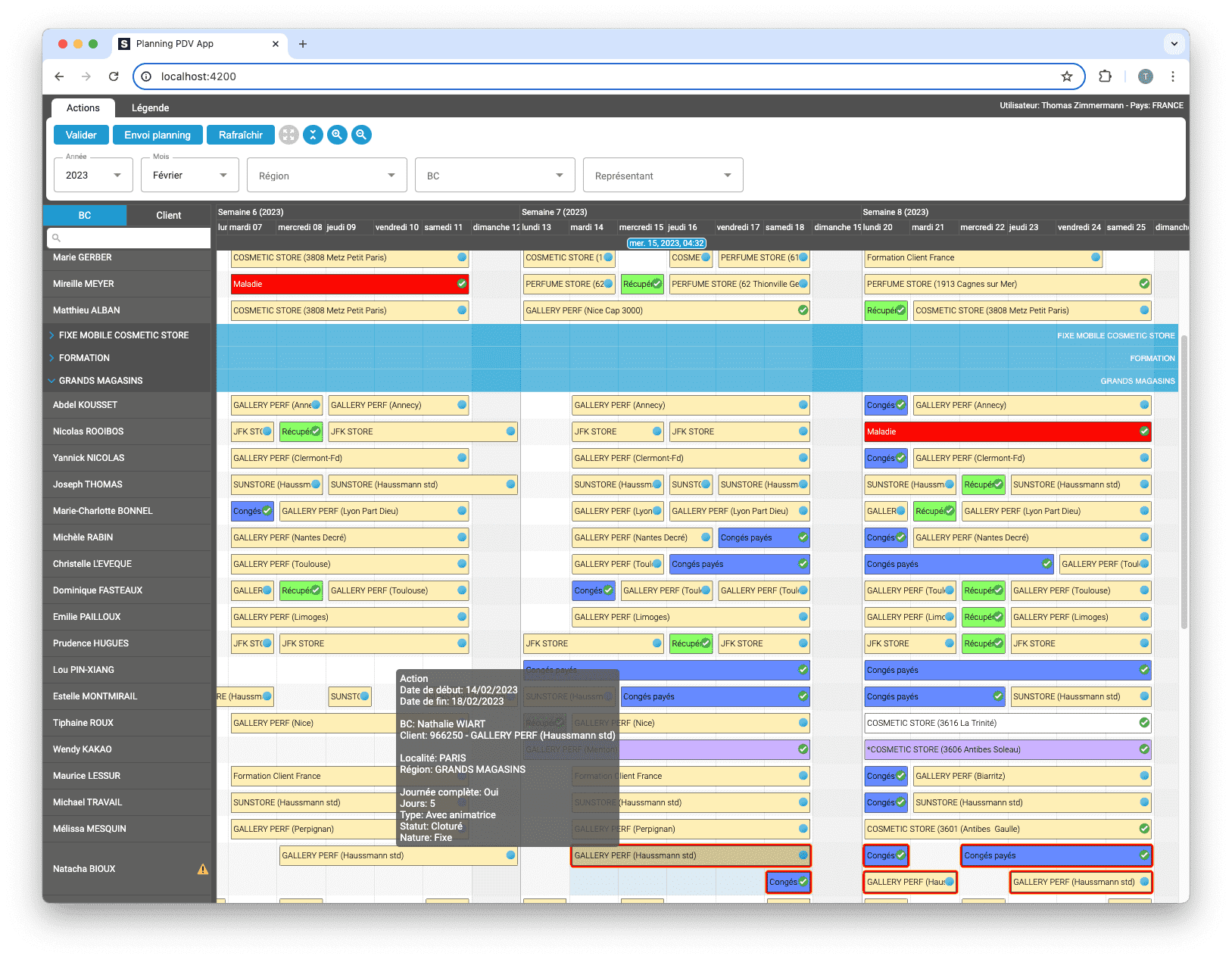
Découvrez comment ScheduleJS s'est intégré en toute transparence à Selligent CRM, améliorant ainsi l'efficacité de la planification pour les consultants d'une grande marque de produits de beauté.
Cet article présente l'intégration d'un composant ScheduleJS dans un tableau Ag-Grid externe, afin de démontrer la flexibilité de ScheduleJS.